The Forex market is a platform for the exchange of currencies from all over the world. Multinational corporations, product manufacturers, big banks use it to convert money from one currency to another. In theory, anyone can participate in the Forex market by changing one currency for another, but it would require lots of capital to see any significant returns. This is where the Forex brokers come in.
Why we need brokers
Online trading brokers give us access to the Forex market, with some added benefits:
Leverage
Leverage is a bit like a mortgage, where you only put down a small deposit and still get the complete house. In Forex, the broker offers you leverage to trade huge amounts of currency with only a small deposit. For example, a 100:1 leverage ratio allows you to control $100,000 worth of trades with only a $1,000 deposit. Besides, leverage can go as high as 1000:1, so you can see the benefit to that. Without leverage, we would not be able to participate in the Forex market, and it is the brokers who provide it.
Access
As mentioned previously, the Forex market is mainly used by big institutions transacting huge amounts of money. Very few individuals can participate at this level, and access to the Forex market is thus denied. The Forex broker, on the other hand, can have enough capital to participate in the interbank market. By law, these brokers are required to have a certain amount of capital, which is enough to grant them access.
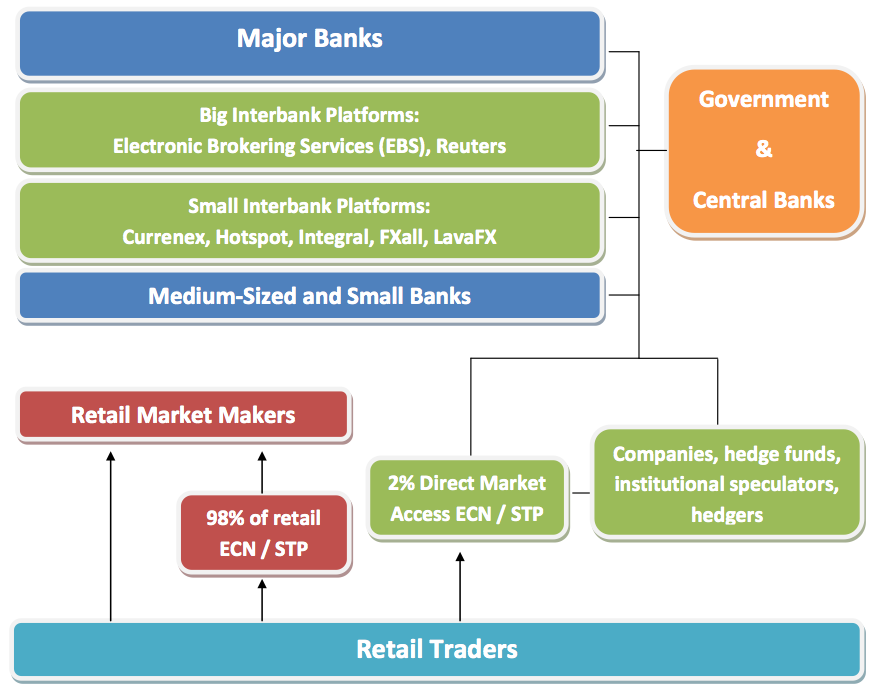
In addition, they have their clients’ deposits which further increase their capital. Apart from the Forex market, some Forex brokers also have access to stock and futures exchanges, which then grants access to traders for trading stocks, futures and other commodities.
None of these would be possible without the brokers, so they are crucial to the retail Forex market. Some great Forex brokers can be found at https://topbrokers.com/forex-brokers or here: http://www.forex-ratings.com.
How do Forex brokers differ?
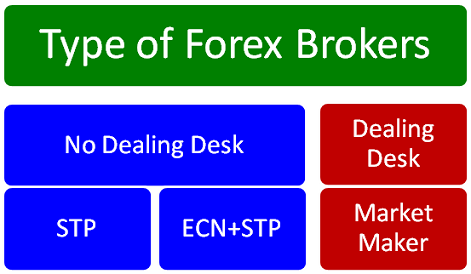
The obvious differences lie in the services they provide and the trading conditions offered to the clients. Some brokers will offer more currency pairs than others, some will require more capital than others; the differences are endless. However, the main difference among Forex brokers is their mode of operation – how they handle their clients’ orders. Here, there are 2 main types of brokers:
Electronic communications network (ECN)
These brokers act as true brokers, because they only match orders from one party to the other and do not handle any of it themselves. This is usually through transferring client orders to liquidity providers, often banks. They only make money from the spread imposed, and have no interest in the clients’ profits.
Market makers
These types of brokers create the market, taking the opposite side of their clients’ trades. In this mode of operation, they make money whenever their clients lose, because they just take the money lost, and they lose whenever a client makes money. Obviously, there is a conflict of interest in this kind of arrangement, although there are still some benefits to dealing with market makers. Slippage, for example, is rare even in volatile market conditions when compared to ECN brokers.
Straight through processing (STP)
STP brokers are a bit of a hybrid in that they will act as market makers to losing clients and ECN brokers to consistent winners because they keep losing money to these clients.
Regardless of which kind of broker you choose, the truth remains to be that you would not be able to even trade in the Forex market without the help of a broker. As such, they are responsible for the expansion of the retail Forex market and crucial to its survival. Quite simply, there would not be a retail Forex market without the brokers.

